Hypogonadism is a medical condition characterized by reduced or absent production of sex hormones. This occurs when the testes in men or the ovaries in women do not function properly. Hormones like testosterone and estrogen play a crucial role in sexual development, metabolism, and overall well-being. When the body does not produce enough of these hormones, it can lead to various health issues, including infertility, fatigue, muscle loss, and mood changes.
There are two primary types of hypogonadism: primary and secondary. Primary hypogonadism results from issues within the testes or ovaries, while secondary hypogonadism stems from problems in the brain, specifically the hypothalamus or pituitary gland, which regulate hormone production. Understanding the root cause is essential for effective treatment, which may include hormone replacement therapy or lifestyle changes.
Key Takeaways
Hypogonadism happens when the body doesn’t make enough testosterone, often leading to low energy, mood changes, and sexual health issues.
There are two types—primary and secondary—each caused by different problems in the testes or brain’s signaling hormones.
Common symptoms include reduced muscle mass, low libido, fatigue, and infertility, which can impact quality of life if left untreated.
Diagnosis usually involves blood tests and a full medical evaluation to pinpoint hormone levels and underlying causes accurately.
Treatment options may include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), lifestyle changes, or medication depending on age and health goals.
Table of Contents
Understanding Hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
Causes of Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism can occur due to various factors, including genetic conditions, medical treatments, or environmental influences. Primary hypogonadism often results from congenital disorders such as Klinefelter syndrome or Turner syndrome, where the sex chromosomes are altered. It can also be caused by injury to the testes or ovaries, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or autoimmune diseases that attack reproductive organs.
Secondary hypogonadism occurs when the hypothalamus or pituitary gland fails to signal the reproductive organs to produce hormones. Causes include tumors, head injuries, chronic stress, obesity, and conditions like Kallmann syndrome. In some cases, excessive opioid or steroid use can also interfere with hormonal regulation.
Symptoms of Hypogonadism
The symptoms vary depending on age and sex. In men, low testosterone levels can lead to decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, reduced muscle mass, and fatigue. Adolescents may experience delayed puberty, leading to a lack of facial and body hair, underdeveloped genitals, and a deep voice failing to develop. Women with hypogonadism may have irregular or absent periods, hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and difficulty conceiving.
In both men and women, hypogonadism can result in osteoporosis, mood disturbances, depression, and cognitive issues. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial to prevent complications and begin appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Hypogonadism
Doctors diagnose hypogonadism through blood tests that measure hormone levels, including testosterone, estrogen, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH). Additional tests, such as imaging studies of the pituitary gland, genetic testing, and semen analysis in men, may help pinpoint the underlying cause.
Treatment Options for Hypogonadism
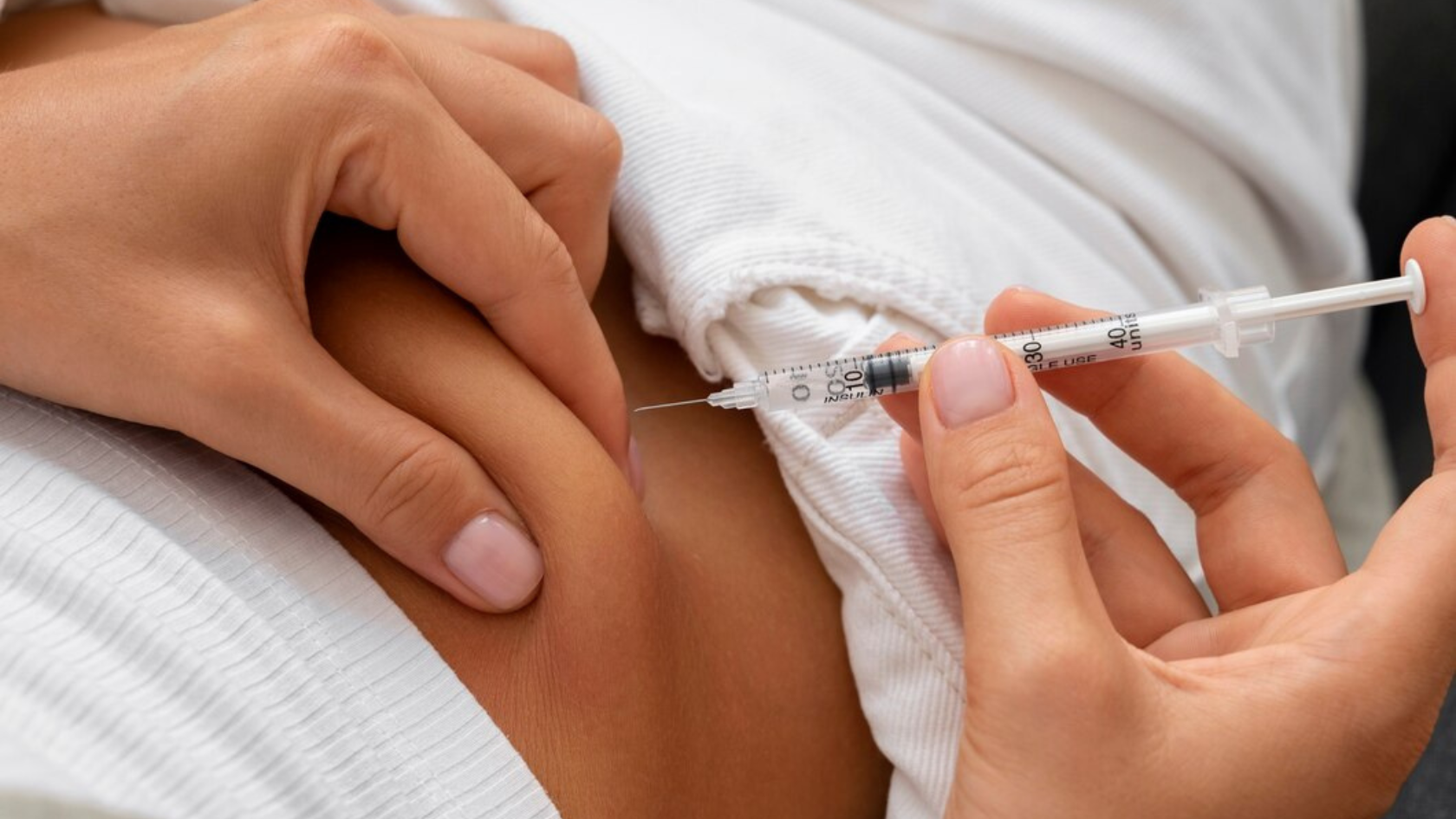
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
For men with low testosterone, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a common treatment. TRT is available in various forms, including injections, patches, gels, and implants. It helps improve energy levels, muscle strength, libido, and mood. However, it requires careful monitoring as it may increase the risk of cardiovascular issues, acne, and prostate enlargement.
Estrogen Therapy for Women
Women with hypogonadism may be prescribed estrogen replacement therapy, often combined with progesterone if they have an intact uterus. This therapy can relieve menopausal symptoms, improve bone health, and enhance overall well-being. However, long-term use may increase the risk of blood clots and certain cancers, so it must be managed under a doctor’s supervision.
Lifestyle and Natural Approaches
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms. A balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and quality sleep support hormone production. Certain supplements like vitamin D, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids may also aid hormone balance. Avoiding excessive alcohol, smoking, and drug use is essential for optimal reproductive health.
Fertility Treatments
For those experiencing infertility, hormone therapy combined with assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or gonadotropin injections may improve the chances of conception. Addressing the underlying hormonal imbalance can restore reproductive function and enhance fertility outcomes.
Struggling with Low Energy & Libido? It Could Be Hypogonadism
Frequently Asked Questions
Hypogonadism is caused by genetic disorders, injury, autoimmune diseases, tumors, obesity, or medical treatments like chemotherapy.
Symptoms include low libido, erectile dysfunction, muscle loss, fatigue, mood changes, and infertility.
Doctors use blood tests to measure hormone levels and may perform imaging or genetic tests to determine the cause.
Yes, treatments include hormone replacement therapy, lifestyle changes, and fertility interventions.
TRT is a treatment for men with low testosterone, available as injections, gels, patches, and implants.
Yes, women with low estrogen levels may experience irregular periods, hot flashes, and infertility.
A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction can support hormone production.
Yes, low hormone levels can affect sperm and egg production, leading to fertility issues.
When managed by a doctor, it is generally safe but may have side effects, including increased cardiovascular risks.
Yes, weight management, proper nutrition, and avoiding harmful substances can improve hormone levels.